An introduction to Leaves
The leaf is responsible for:
- Allows tree to breathe
- Helps provide food for animals
- Release oxygen into the air
parts of a Leaf
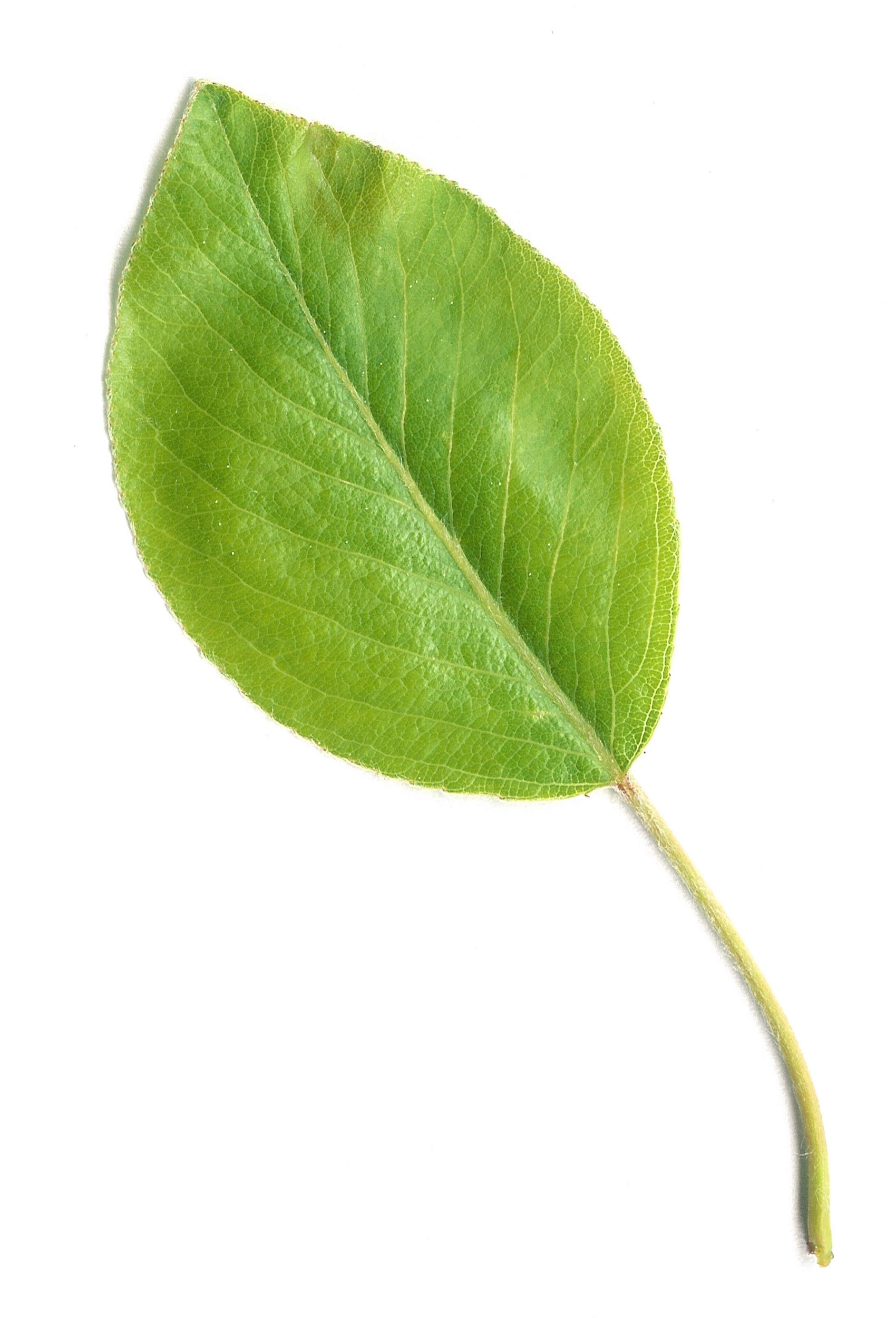
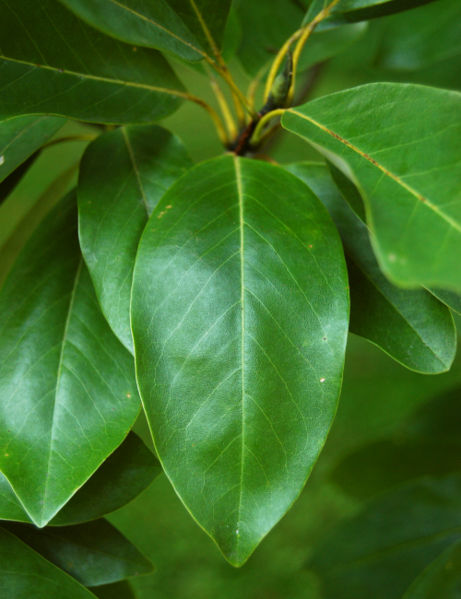
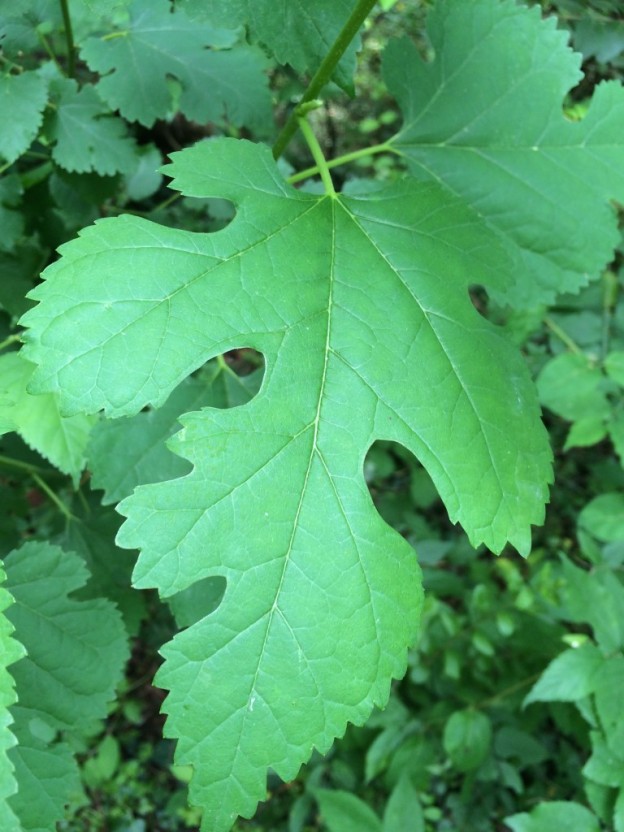
The Blade : this is the body of the leaf
The Apex : this is the tip of the leaf
The Margin : this is the outer edge of the leaf
The Petiole : this is the long narrow stem connecting the leaf to the branch
The Midrib : this is the center of the leaf, dispersing water from the branch to the leaf, and food from the leaf to the tree
The Base : this connects the Midrib to the Petiole
Leaf Types
Leaves can be classified how the Petiole is attached :
- Simple leaves – single petiole attached to a single base
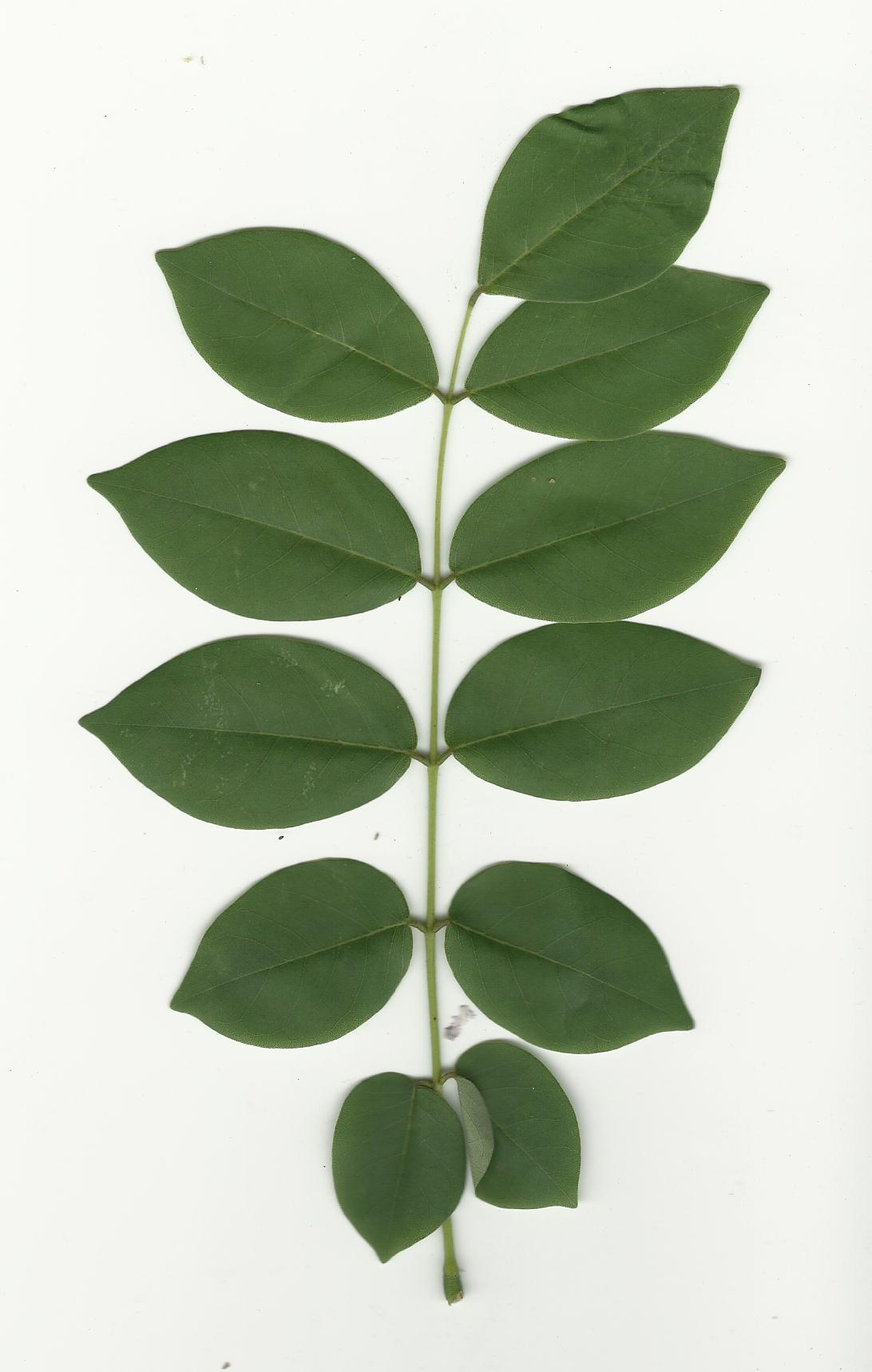
- Compound leaves – Single petiole with many leaf blades
- Double compound leaves – Many petioles with other petioles attaching to them
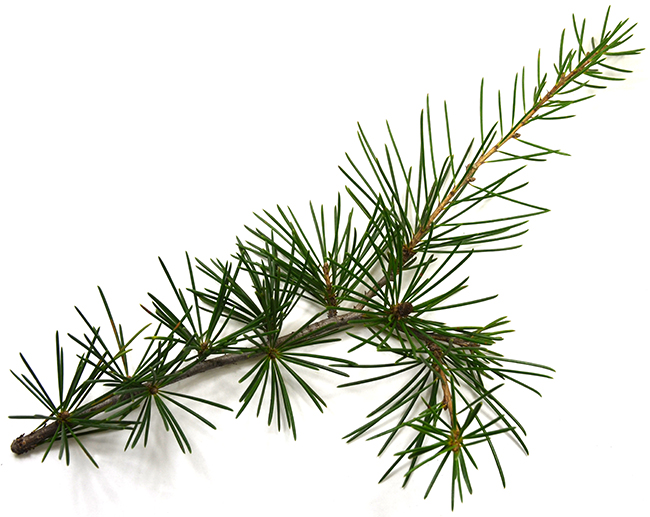
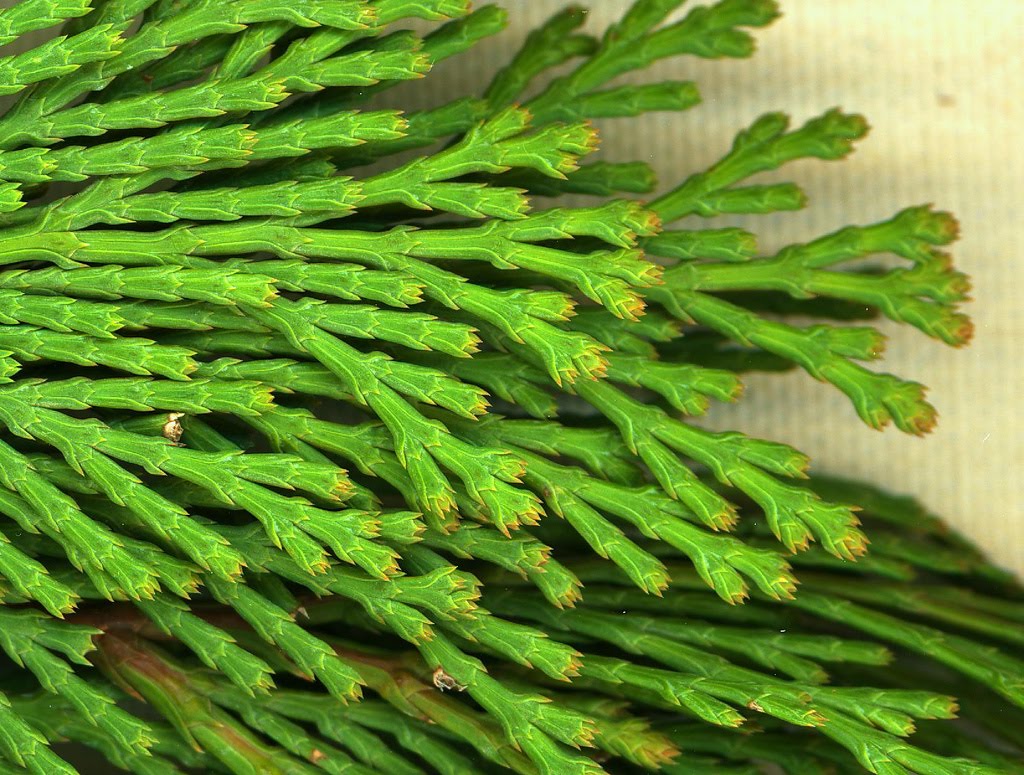
- Needle leaves – long thin and pointed, they are either square or flat
Leaf Body Shape
So many leaf shapes that help us identify trees!
- Linear
- Oblong
- Ovate
- Cordate
- Deltoid
- Orbiculate
For needle leaves we are only concerned with the following two:
- 4 sided needle
- Flattened
Leaf Margin Shapes
So many leaf margins to also help identify trees!
- Smooth
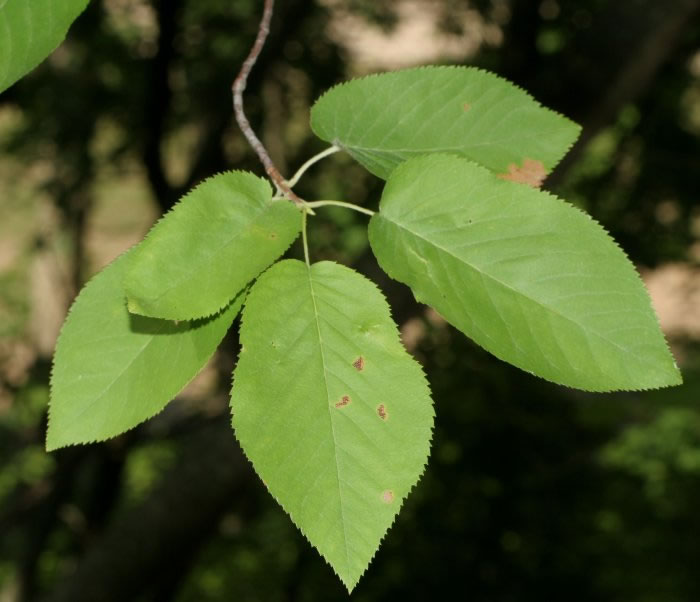
- Fine toothed
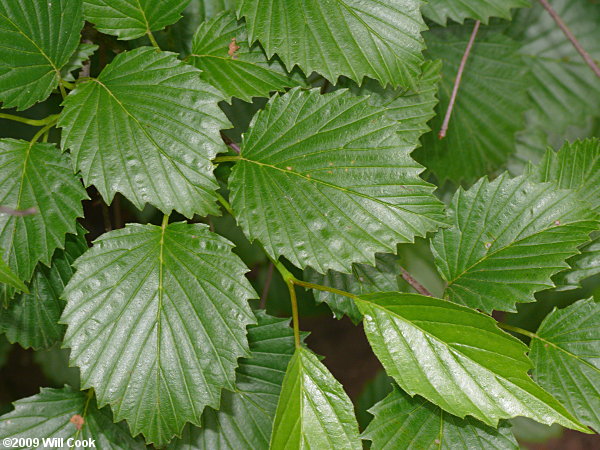
- Course toothed
- Lobed
Leaf Veining
Two types of leaf veining:
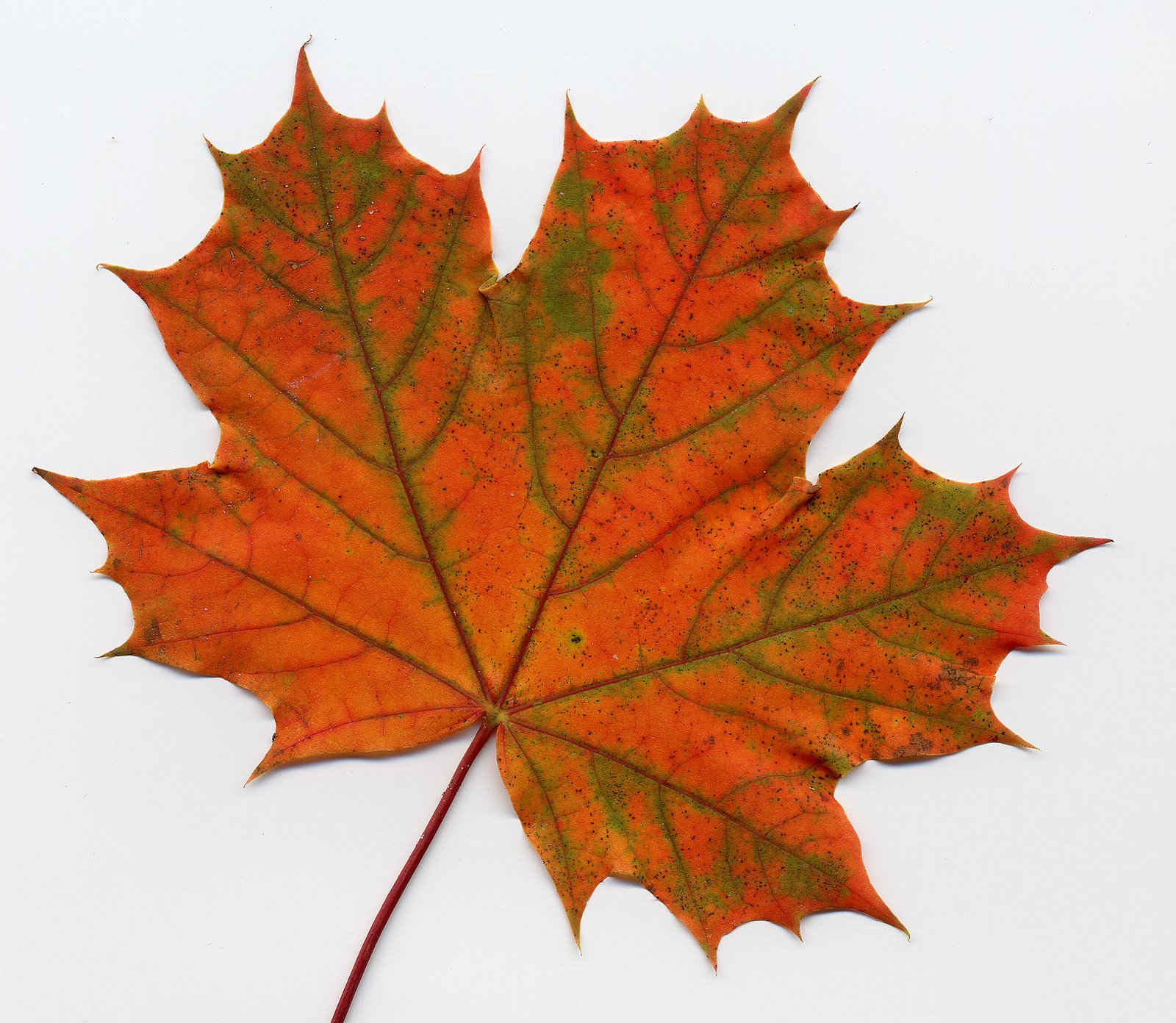
- Palmately Veined (many midribs, ex. Maple Leaf)
- Pinnately Veined (one midrib, ex Simple Leaf)
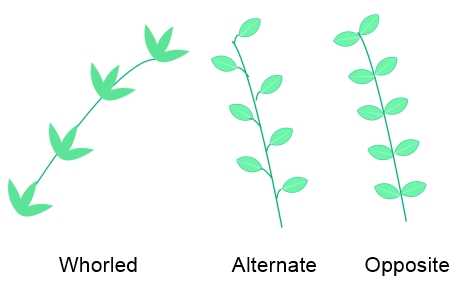
Leaf Arrangement on a Branch
How leafs are attached to the petiole is called leaf arrangement:
Needle leaf classification based on arrangement
• Bundle of 2
• Bundle of 5
• Single on a twig
• Scale like
• Clusters
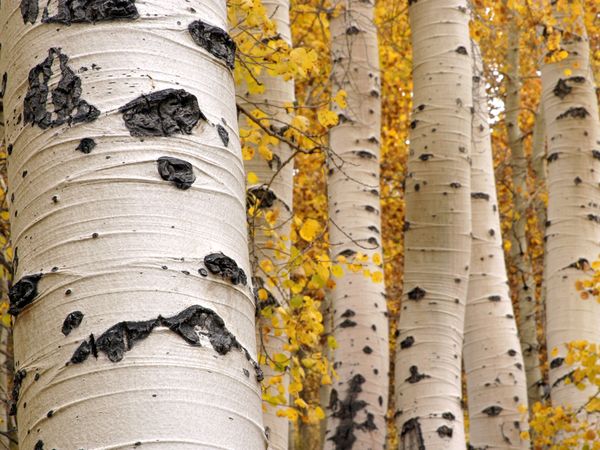
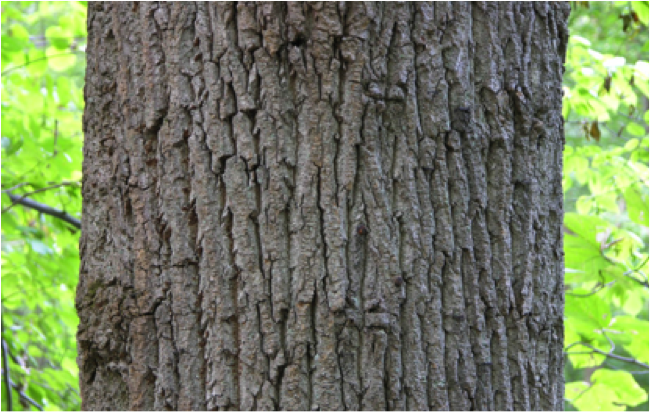
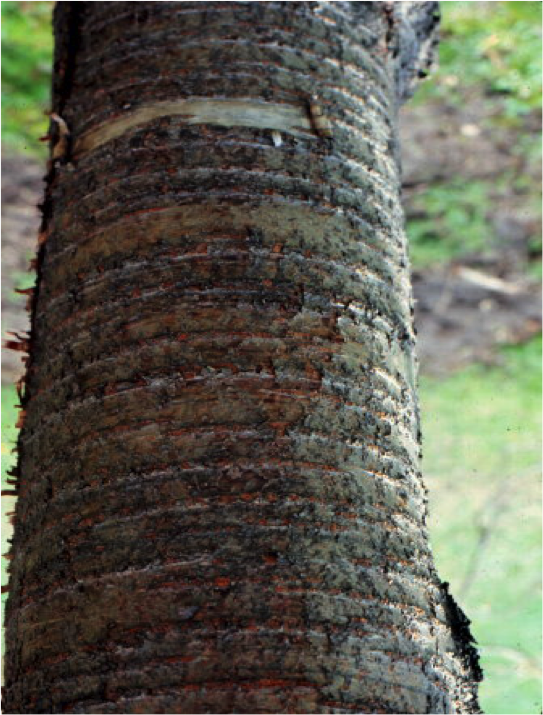
Types of Tree Bark
- Scaly Patches
- Smooth Bark
- Vertical Bark
- Horizontal Bark
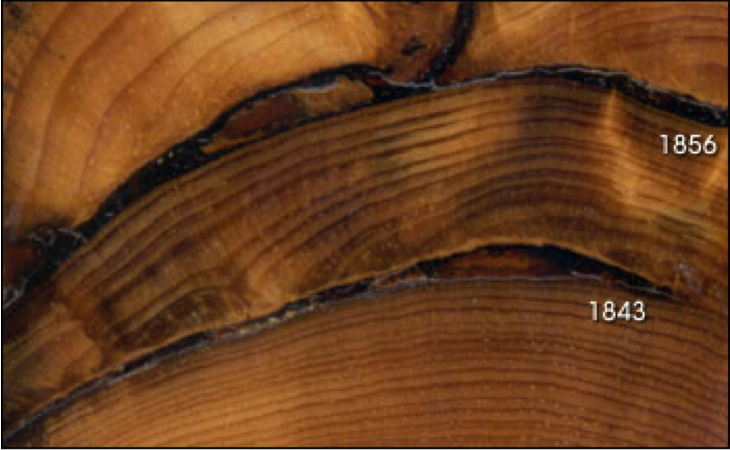
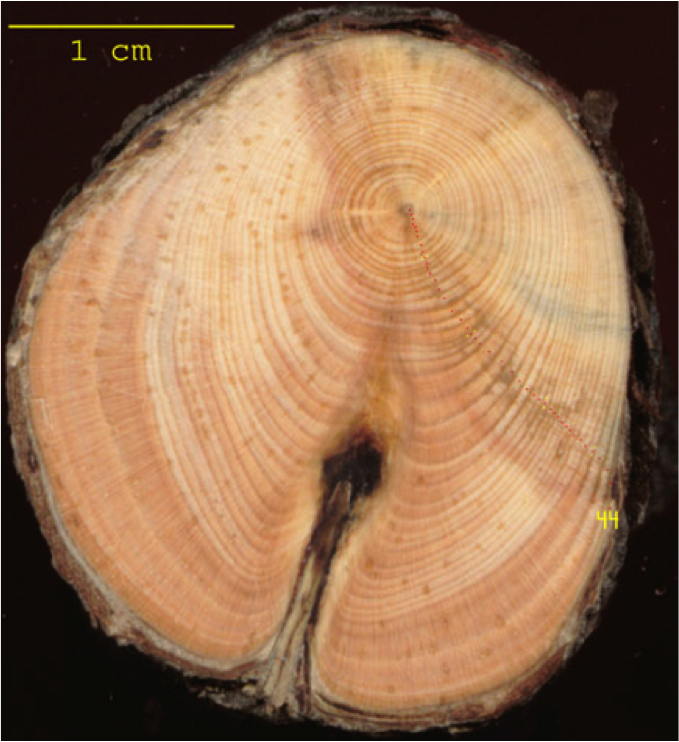
Tree Rings
Every year trees grow in diameter leaving a visible mark called a tree ring.
By studying tree rings we can tell a lot about a tree's past health and growing conditions:
- Tree age
- Seasonal growing conditions (drought)
- Pest population
- Forest fires
- Changes in surroundings
A closer look at tree cookies
When observing tree rings look at the following:
Width of a tree ring:
- Thick rings mean high amount of growth (lots of sun and water)
- Thin rings mean low amount of growth (drought)
Uneven growth rings:
- Tree grew on a slope
- Tree was crowded on the narrow side of the tree rings
Char marks between tree rings:
- Scars of a forest fire
Narrow holes in the bark or sapwood:
- Insects have eaten part of this tree
Dichotomous Key
A dichotomous key is used to identify things based on characteristics. It works by looking for the characteristics of something and following a branch until you end up with the information you need.
Now a tree dichotomous key: