Heat & temperature
Early scientists believed that heat was a fluid.
Eventually, they determined that heat is a form of energy that comes from the movement of many tiny particles.
Particle model Theory
- All matter is made up of particles that are much too small to be seen.
- The particles are always in motion.
- They vibrate, rotate, and (in liquids and gases) move from place to place.
- The particles have empty spaces between them.
Heat changes the speed of moving particles of matter. Transferring heat to a substance increases the movement or kinetic energy of the particles in that substance.
Kinetic Energy:
Energy that a particle possesses by being in motion.
States of matter
All matter exists in various forms, we call these forms states of matter. All matter changes its form depending on the kinetic energy of particles within it.
Solid:
- Particles are attached to each other in all directions.
- Solid having a definite shape and volume (Volume is the amount of space that matter occupies)
- Solids are very limited in their movement.
Liquid:
- Particles in the liquid state are only loosely attached to each other and they can easily slip past each other.
- Liquids takes the shape of its container.
- Empty spaces between particles in a liquid are usually larger than those in a solid.
Gas:
- Particles of matter in a gas state are not connected to one another. These particles have the greatest freedom of movement - high levels of kinetic energy.
- Gas fills the empty space of a container. A gas has no set shape.
- The spaces between particles in a gas state are much larger than those in either a solid or a liquid.
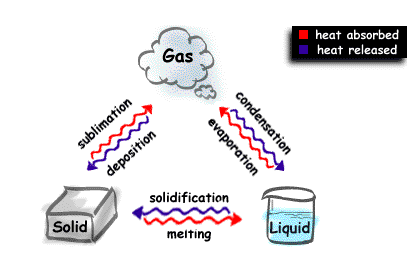
Changes of state of matter
Heat and Temperature
Temperature:
- Temperature indicates the average energy (speed) kinetic energy - of the particles in motion in a substance.
- Gauges how hot or cold matter is.
Thermal Energy:
- Total kinetic energy of all the particles the substance contains
- Which has the greater thermal energy, the tea cup or tea pot?
Joule:
Measurement of heat energy
Heat :
- Is the energy that transfers from a substance whose particles have a higher kinetic energy to a substance who particles have a lower kinetic energy.
The more heat you add to matter the faster its particles move, therefore its temperature increases!
Why does it move?
Difference in kinetic energy- Always from high energy to low energy
Cold
- Is a lack of thermal energy
GALILEO'S THERMOMETER
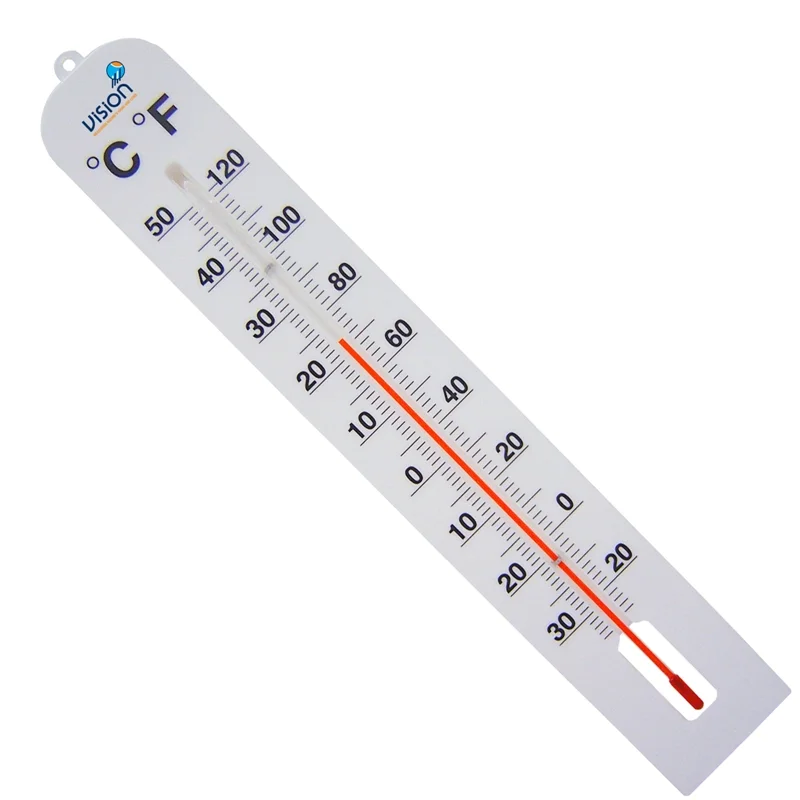
Thermometer:
Fahrenheit Scale : USA
Celsius Scale : Every country but USA
How Energy is transferred
Thermal expansion :
- As matter is heated (energy is transferred) the temperature rises and the spaces between particles increases, this is thermal expansion.
- Thermal expansion decreases density
This very concept fuelled the industrial revolution, Steam power!!
Ever wonder how a thermometer's red liquid rises?
Conduction:
- Transfer of heat energy between substances that are touching each other
Conductors:
- Materials that allow easy transfer of heat, good conducting materials are those materials where there is little space between the particles AKA the material is highly dense.
- Metals - good conductor
- Water - good conductor
- Plastic - poor conductor
- Air - poor conductor
Conductivity:
Material's ability to transfer heat via conduction
Insulators:
- Materials that do not easily allow heat transfer have a lot of space between particles AKA the material is not very dense
- Air
- Plastic
- Glass
Convection:
Thermal energy can be transferred in fluids & gases, by the circular motion of the particles.
In convection, the warmer particles transfer their energy to the cooler particles as they move in a circular pattern, called a ‘convection’ current.
Radiation:
- The emission of energy as electromagnetic waves
- Heat is released at a relatively low level of radiation called infrared radiation
- Radiant energy does not rely on the movement of particles to transfer its energy
- Waves of radiant energy can travel in a vacuum. All waves travel, across empty space, at an extremely high speed
The Electro-Magnetic Spectrum
THE SUN EMITS VARIOUS WAVELENGTHS OF ENERGY
Some surfaces absorb or reflect infrared wavelengths depending on some characteristics:
- Light & shiny - Reflect heat
- Dark & dull - Absorb heat
Draw a Lava lamp and point out where convection, conduction, and radiation take place.